Perio diagnosis staging and grading are essential components of periodontal assessment, providing a comprehensive understanding of the severity and extent of periodontal disease. This in-depth guide explores the principles and applications of these systems, empowering clinicians to make informed treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
Periodontal diagnosis involves a thorough clinical examination, including probing, charting, and radiographic evaluation. Staging classifies the extent of disease based on clinical parameters, while grading assesses the severity of tissue destruction. Together, these systems provide a holistic view of periodontal status, guiding treatment planning and monitoring disease progression.
Perio Diagnosis: Perio Diagnosis Staging And Grading
Periodontal diagnosis is the process of identifying and classifying periodontal diseases. It is an essential step in developing a treatment plan and assessing the prognosis for periodontal health. Periodontal diagnosis is based on a comprehensive clinical examination, which includes visual inspection, probing, and radiographic evaluation.
Clinical Examination Procedures
The clinical examination procedures used in periodontal diagnosis include:
- Visual inspection:The clinician examines the teeth and gums for signs of inflammation, bleeding, and recession.
- Probing:The clinician uses a periodontal probe to measure the depth of the periodontal pockets and assess the attachment loss.
- Radiographs:Radiographs are used to assess the extent of bone loss and to identify any underlying pathology.
Role of Radiographs
Radiographs play an important role in periodontal diagnosis by providing information about the extent of bone loss and the presence of any underlying pathology. Radiographs can be used to:
- Detect bone loss:Radiographs can show the extent of bone loss around the teeth, which can help the clinician to assess the severity of the periodontal disease.
- Identify underlying pathology:Radiographs can also be used to identify any underlying pathology, such as cysts, tumors, or foreign bodies, which may be contributing to the periodontal disease.
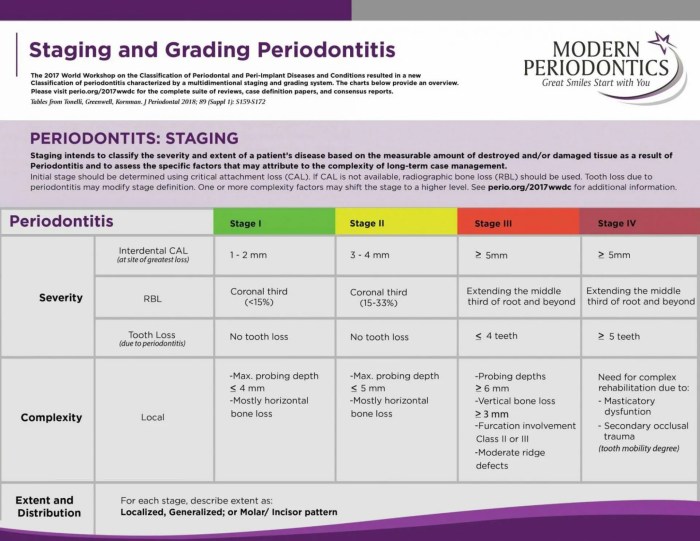
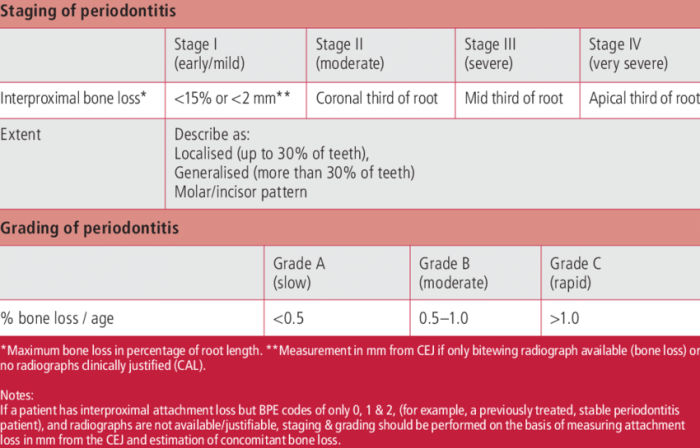
Perio Staging
Periodontal staging is a system used to classify the severity of periodontal disease based on the extent of tissue destruction and the presence of specific clinical signs and symptoms.
Stages of Periodontal Disease
- Stage I (Early Gingivitis):Mild inflammation of the gingiva, characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding upon probing.
- Stage II (Moderate Gingivitis):More severe inflammation, with increased bleeding, swelling, and the presence of calculus and plaque.
- Stage III (Early Periodontitis):Loss of attachment and bone loss, with increased probing depths and bleeding, and the formation of periodontal pockets.
- Stage IV (Moderate Periodontitis):Significant bone loss, with increased probing depths, mobility of teeth, and the presence of abscesses and/or furcation involvement.
- Stage V (Advanced Periodontitis):Severe bone loss, with deep probing depths, severe mobility of teeth, and the presence of multiple abscesses and/or furcation involvement.
Criteria for Determining the Stage of Periodontal Disease
- Clinical examination, including probing depths, bleeding on probing, and assessment of attachment loss.
- Radiographic examination, to assess the extent of bone loss.
- Patient history, including smoking, diabetes, and other risk factors.
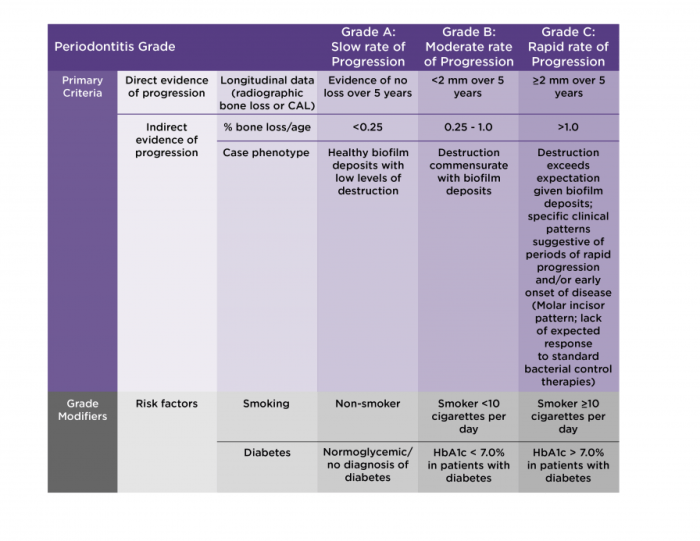
Perio Grading
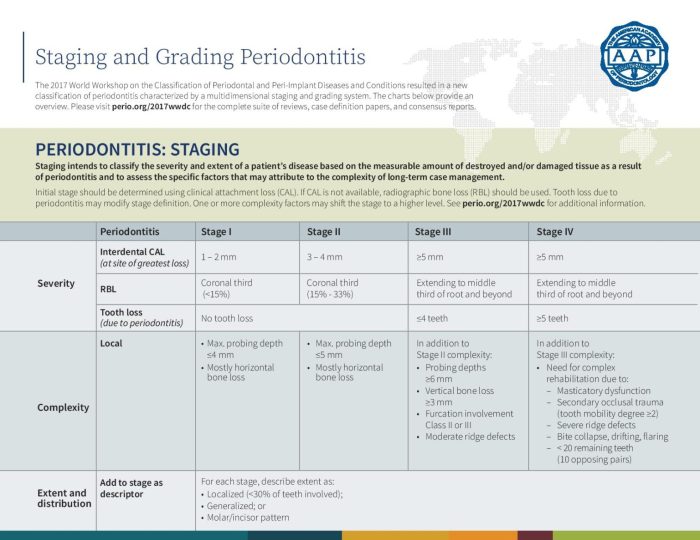
Periodontitis is a disease that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. Periodontitis is a major cause of tooth loss in adults. Periodontitis is classified into different stages and grades based on the severity of the disease.
Periodontitis grading refers to the assessment of the extent and severity of periodontal tissue destruction, specifically focusing on the loss of periodontal attachment and alveolar bone support.
Criteria for Determining Periodontitis Grading
The grading of periodontitis is based on the following criteria:
- Loss of periodontal attachment (clinical attachment level, CAL)
- Radiographic evidence of alveolar bone loss
- Clinical signs of inflammation (gingival redness, swelling, bleeding on probing)
- Presence of periodontal pockets
- Mobility of teeth
The combination of these factors is used to determine the grade of periodontitis, with higher grades indicating more severe disease.
Comparison of Staging and Grading
Periodontal staging and grading are two distinct systems used to assess the severity of periodontal disease. Staging describes the extent of disease progression, while grading indicates the degree of tissue destruction.
Staging is based on clinical parameters such as probing depth, attachment loss, and radiographic findings. It is a relatively simple system that provides a general overview of disease severity. Grading, on the other hand, is based on histologic criteria and involves a more detailed examination of the periodontal tissues.
It allows for a more precise assessment of tissue destruction and can be used to monitor disease progression over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Staging has the advantage of being simple and easy to perform. It can be used in a clinical setting without the need for specialized equipment or training. However, staging is limited in its ability to provide detailed information about tissue destruction.
Grading has the advantage of providing a more precise assessment of tissue destruction. It can be used to identify early signs of disease and to monitor disease progression over time. However, grading is more complex and time-consuming to perform than staging, and it requires specialized equipment and training.
Complementary Use
Staging and grading can be used together to provide a comprehensive assessment of periodontal disease. Staging provides a general overview of disease severity, while grading provides a more detailed assessment of tissue destruction. By combining these two systems, clinicians can gain a better understanding of the extent and severity of periodontal disease and can develop more effective treatment plans.
Implications for Treatment Planning
Periodontal staging and grading provide crucial information for developing customized treatment plans for patients. These parameters help clinicians assess the severity and extent of periodontal disease, enabling them to tailor interventions specifically to each individual’s needs.
By understanding the stage and grade of periodontal disease, clinicians can determine the appropriate treatment modalities, establish realistic goals, and predict the prognosis. Staging and grading guide decisions regarding the intensity and duration of therapy, including surgical and non-surgical interventions.
Treatment Plan Customization, Perio diagnosis staging and grading
- Early Stage Disease:Conservative treatment options such as scaling and root planing, oral hygiene instruction, and regular monitoring may be sufficient.
- Moderate Stage Disease:More aggressive interventions may be necessary, including periodontal surgery, antibiotics, and regenerative procedures.
- Advanced Stage Disease:Extensive treatment is typically required, involving multiple surgeries, bone grafting, and potentially tooth extraction.
Treatment Decision Guidance
- Staging:Determines the extent of disease spread and bone loss, guiding decisions on the need for surgical intervention and the type of surgery required.
- Grading:Assesses the inflammatory response and tissue destruction, informing decisions on the severity of treatment and the need for antibiotics or regenerative therapies.
Case Studies
Case studies provide valuable insights into the practical application of periodontal staging and grading in clinical settings. They illustrate the challenges and successes encountered in utilizing these systems and demonstrate how they can be instrumental in improving patient outcomes.
Challenges and Successes
One challenge in using staging and grading systems is the variability in interpretation among clinicians. To address this, standardized criteria and training programs have been developed to ensure consistency in diagnosis. Additionally, the use of technology, such as digital radiography and periodontal probes, can enhance the accuracy of assessments.
Successes in using staging and grading systems include improved communication between clinicians and patients, enhanced decision-making for treatment planning, and more accurate prognoses. By providing a comprehensive assessment of periodontal health, these systems enable clinicians to tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs, leading to better outcomes.
Improving Patient Outcomes
Staging and grading systems play a crucial role in improving patient outcomes by:
- Identifying patients at risk for periodontal disease progression
- Monitoring disease progression and response to treatment
- Guiding treatment decisions and tailoring interventions to specific patient needs
- Facilitating communication between clinicians and patients, ensuring a shared understanding of the disease and its management
By utilizing staging and grading systems, clinicians can provide more personalized and effective care, leading to improved periodontal health and overall well-being for patients.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between staging and grading in periodontal disease?
Staging classifies the extent of disease based on clinical parameters, while grading assesses the severity of tissue destruction.
How are staging and grading used in treatment planning?
Staging and grading provide guidance on the type and intensity of treatment required, ensuring a customized approach for each patient.
What are the advantages of using both staging and grading?
Combining staging and grading provides a comprehensive assessment of periodontal disease, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment decisions.