Compute the total overhead cost applied to job 205 – Understanding the total overhead cost applied to Job 205 is crucial for accurate job costing and profitability analysis. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of overhead cost calculation, allocation, and its impact on job profitability, providing a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with Job 205.
This guide explores the various methods used to calculate overhead costs, identifies the key components that make up these costs, and explains the different methods used to allocate them to specific jobs. Additionally, it analyzes the impact of overhead costs on the total cost and profitability of Job 205, providing valuable insights for effective cost management.
Overhead Cost Calculation for Job 205
Overhead costs are indirect costs that cannot be directly traced to a specific cost object. They are typically applied to jobs using an overhead rate, which is calculated by dividing the total overhead costs by the total direct labor hours or other appropriate allocation base.
There are several methods for calculating overhead costs, including:
- Activity-based costing (ABC)
- Traditional costing methods (e.g., direct labor hours, machine hours, unit-based)
- Industry-specific methods (e.g., retail method, restaurant method)
The choice of overhead cost calculation method depends on the nature of the business and the availability of data.
Overhead Cost Components
Overhead costs can be classified into two main categories:
- Direct costs: These costs can be directly traced to a specific cost object. Examples include raw materials, direct labor, and freight-in.
- Indirect costs: These costs cannot be directly traced to a specific cost object. Examples include rent, utilities, and administrative salaries.
The following table summarizes the different components of overhead costs:
| Cost Component | Type | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Indirect materials | Indirect | Office supplies, cleaning supplies |
| Indirect labor | Indirect | Supervisors’ salaries, maintenance workers’ salaries |
| Utilities | Indirect | Electricity, gas, water |
| Rent | Indirect | Factory rent, office rent |
| Depreciation | Indirect | Depreciation on factory equipment, office equipment |
| Insurance | Indirect | Factory insurance, office insurance |
| Administrative salaries | Indirect | Salaries of administrative staff, clerical staff |
Overhead Cost Allocation

Once the overhead costs have been calculated, they must be allocated to the cost objects. This can be done using a variety of methods, including:
- Activity-based costing (ABC)
- Simple allocation methods (e.g., direct labor hours, machine hours, unit-based)
- Indirect cost pools
The choice of overhead cost allocation method depends on the nature of the business and the availability of data.
The following steps are involved in allocating overhead costs:
- Identify the cost objects.
- Choose an overhead cost allocation method.
- Calculate the overhead rate.
- Apply the overhead rate to the cost objects.
The factors that influence overhead cost allocation include:
- The nature of the business
- The availability of data
- The accuracy of the overhead cost calculation
Impact of Overhead Cost on Job 205: Compute The Total Overhead Cost Applied To Job 205
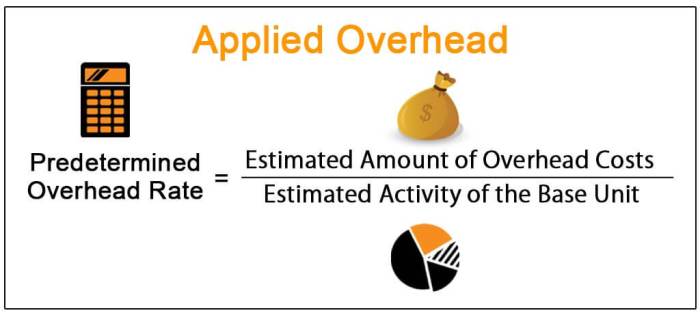
Overhead costs have a significant impact on the total cost of Job 205. The overhead rate used to allocate overhead costs to Job 205 is 150%. This means that for every direct labor hour worked on Job 205, $150 of overhead costs are applied.
The following table shows a detailed breakdown of the overhead costs applied to Job 205:
| Cost Component | Amount |
|---|---|
| Indirect materials | $1,000 |
| Indirect labor | $2,000 |
| Utilities | $500 |
| Rent | $1,000 |
| Depreciation | $500 |
| Insurance | $200 |
| Administrative salaries | $1,000 |
| Total overhead costs | $6,200 |
The total overhead costs applied to Job 205 are $6,200. This represents a significant portion of the total cost of the job.
Strategies for Reducing Overhead Costs
There are a number of strategies that businesses can use to reduce overhead costs. These strategies include:
- Outsourcing: Outsourcing non-core activities to third-party providers can help businesses reduce overhead costs.
- Lean manufacturing: Lean manufacturing techniques can help businesses reduce waste and improve efficiency, which can lead to lower overhead costs.
- Technology: Technology can be used to automate tasks and improve efficiency, which can lead to lower overhead costs.
- Negotiation: Businesses can negotiate with suppliers and vendors to reduce the cost of goods and services.
- Budgeting: Budgeting can help businesses track and control their overhead costs.
The best strategy for reducing overhead costs will vary depending on the nature of the business and the specific circumstances.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the different methods used to calculate overhead costs?
Common methods include activity-based costing, absorption costing, and variable costing.
How are overhead costs allocated to specific jobs?
Overhead costs can be allocated based on direct labor hours, machine hours, or other relevant allocation bases.
What is the impact of overhead costs on job profitability?
Overhead costs can significantly impact job profitability by increasing the total cost of the job and reducing the profit margin.