Welcome to the fascinating world of salt in a chem lab crossword! This guide will immerse you in the captivating realm of chemistry, where salt plays a pivotal role in a myriad of laboratory procedures. Get ready to unravel the secrets of this essential substance and conquer those crossword puzzles with ease.
As we delve into the topic, we’ll explore the diverse types of salt found in a chemistry lab, their chemical formulas, and their unique properties. We’ll also uncover the crucial role salt plays in precipitation reactions, acid-base titrations, and buffer solutions.
Types of Salt in a Chemistry Lab
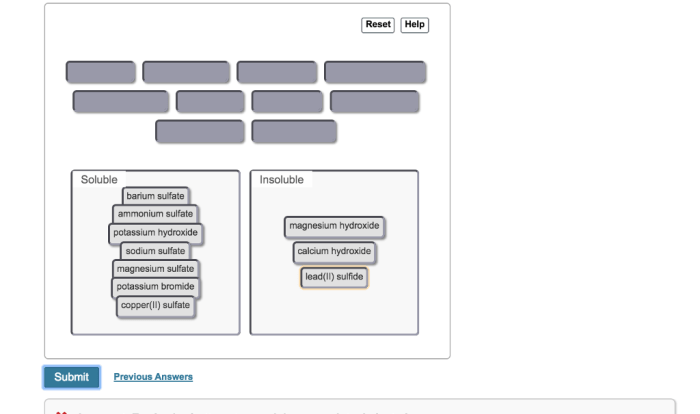
Salts are ionic compounds that form when a metal reacts with a non-metal. They are typically crystalline solids that are soluble in water. There are many different types of salts, each with its own unique properties.
Some of the most common salts found in a chemistry lab include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3)
- Copper sulfate (CuSO4)
Sodium chloride is the most common salt in the world. It is also known as table salt and is used to flavor food. Potassium nitrate is a white, crystalline solid that is used as a fertilizer and in the production of gunpowder.
Copper sulfate is a blue, crystalline solid that is used as a fungicide and in the production of blue dyes.
Chemical Formulas and Properties
The chemical formula of a salt indicates the ratio of the metal and non-metal ions in the compound. For example, the chemical formula of sodium chloride is NaCl, which means that there is one sodium ion (Na+) for every chloride ion (Cl-).
The chemical formula of potassium nitrate is KNO3, which means that there is one potassium ion (K+) for every nitrate ion (NO3-). The chemical formula of copper sulfate is CuSO4, which means that there is one copper ion (Cu2+) for every sulfate ion (SO42-).
The properties of a salt depend on the metal and non-metal ions that make up the compound. For example, sodium chloride is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Potassium nitrate is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water and has a slightly bitter taste.
Copper sulfate is a blue, crystalline solid that is soluble in water and has a metallic taste.
Uses of Salt in a Chemistry Lab

Salt, commonly known as sodium chloride (NaCl), plays a crucial role in various laboratory procedures and chemical reactions. Its unique properties make it an essential reagent for precipitation reactions, acid-base titrations, and the preparation of buffer solutions.
Precipitation Reactions
Salt is often used to induce precipitation reactions, where ions in a solution combine to form an insoluble solid precipitate. By adding a salt solution to another solution containing the appropriate ions, a precipitate can be formed. This technique is commonly employed in qualitative analysis to identify and separate different ions present in a solution.
Acid-Base Titrations
Salt solutions can be used as titrants in acid-base titrations. A titrant is a solution of known concentration that is added to another solution of unknown concentration to determine its concentration. Salt solutions, such as sodium chloride, are often used in titrations involving weak acids or bases, where the endpoint can be more easily observed due to the formation of a precipitate.
Buffer Solutions
Salt solutions can be used to prepare buffer solutions, which are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. Buffer solutions are essential for maintaining a stable pH in various chemical and biological reactions.
By adding a salt solution to a weak acid or base, the pH of the solution can be adjusted and maintained within a desired range.
While working on a crossword puzzle in chem lab, I got stuck on a clue about salt. To clear my mind, I decided to take a break and read about the act of contrition in Spanish . After learning about this important prayer, I felt refreshed and ready to return to my crossword puzzle.
I quickly solved the clue about salt, feeling satisfied with my newfound knowledge and renewed focus.
Effects on Solubility, Conductivity, and pH
The addition of salt to a solution can affect its solubility, conductivity, and pH. Salt can increase the solubility of some compounds, such as ionic compounds, by disrupting the electrostatic interactions between the ions. It can also increase the conductivity of a solution by providing additional ions that can carry electric current.
Additionally, salt can affect the pH of a solution, depending on the nature of the salt and the solution it is added to.
Safety Precautions When Handling Salt in a Chemistry Lab
Salt, commonly known as sodium chloride (NaCl), is a widely used chemical in chemistry labs. While generally considered harmless, it is essential to handle salt with proper precautions to prevent potential hazards.
The most common risks associated with handling salt in a chemistry lab include skin irritation, eye damage, and inhalation risks. Salt can cause skin irritation due to its drying effect, which can lead to redness, itching, and discomfort. Exposure to salt dust or aerosols can also irritate the eyes, causing redness, watering, and discomfort.
In severe cases, inhalation of salt dust can lead to respiratory irritation, coughing, and difficulty breathing.
Safe Handling of Salt
To ensure safe handling of salt in a chemistry lab, it is crucial to follow proper procedures. Firstly, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, lab coats, and safety glasses when handling salt. Avoid direct skin contact with salt, and use a scoop or spatula to transfer it.
If salt comes into contact with skin, rinse the affected area thoroughly with water.
Safe Storage of Salt, Salt in a chem lab crossword
Salt should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated area, away from sources of heat and moisture. Keep salt containers tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption and contamination. Label all salt containers clearly to avoid confusion with other chemicals.
Safe Disposal of Salt
Dispose of salt waste according to your institution’s guidelines. In general, small amounts of salt can be disposed of down the drain with plenty of water. However, larger quantities should be disposed of through a hazardous waste disposal service.
Applications of Salt in Chemistry Beyond the Lab

Salt, beyond its indispensable role in the laboratory, finds extensive applications in industries and commercial sectors. Its unique properties make it a versatile substance with a wide range of uses.
One of the most significant applications of salt is in food preservation. The ability of salt to inhibit microbial growth has been known for centuries. In the food industry, salt is used to preserve meat, fish, and vegetables by drawing out moisture and creating an unfavorable environment for bacteria.
This process, known as salting or curing, extends the shelf life of food products and prevents spoilage.
Water Softening
Salt is also widely used in water softening. Hard water, which contains high levels of calcium and magnesium ions, can cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Salt, in the form of sodium chloride, is used in water softeners to exchange calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions.
This process results in softened water, which is less likely to cause scaling and improves the efficiency of water-using appliances.
Road Deicing
During winter months, salt is extensively used for road deicing. Salt lowers the freezing point of water, preventing ice formation on roads and sidewalks. This helps maintain safe driving conditions and reduces the risk of accidents. However, the use of salt for deicing can have environmental implications, which will be discussed in the following section.
FAQ Corner: Salt In A Chem Lab Crossword
What are some common types of salt found in a chemistry lab?
Sodium chloride, potassium nitrate, and copper sulfate are some of the most commonly encountered salts in a chemistry lab.
How does salt affect the solubility of solutions?
The presence of salt can increase or decrease the solubility of other substances in a solution, depending on the specific salt and solute.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling salt in a chemistry lab?
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and eye protection, when handling salt in a chemistry lab. Avoid contact with skin and eyes, and never ingest salt.